basal tear secretion test|The Tearing Patient: Diagnosis and Management : distribution There are two variations of the Schirmer test: Schirmer I measures total tear secretion (basal and reflex). Schirmer II is a measure of reflex secretion only and involves . According to new research being conducted at the Stony Brook University MART building, dry heat ovens have been shown to be effective for disinfecting N95 masks.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Remove the tube or bottle contents and place the rotor upside-down in an autoclave. Autoclave at 121°C for about 30 minutes. At the end of the autoclave cycle the tube or bottle material should .
The Tearing Patient: Diagnosis and Management
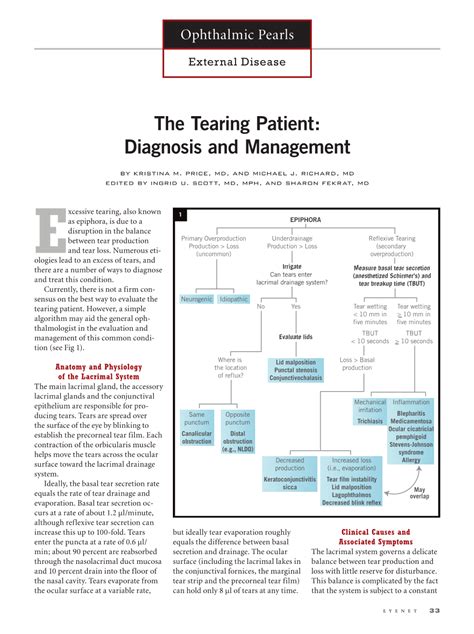
The Schirmer tear test assesses the amount of tears in the eyes and is frequently used to diagnose dry eye syndrome. Basal and reflex tear . There are two variations of the Schirmer test: Schirmer I measures total tear secretion (basal and reflex). Schirmer II is a measure of reflex secretion only and involves . There is some debate about the reliability of testing to evaluate tear production, but we find it useful to assess the basal tear secretion. This is done by placing a strip of filter paper .
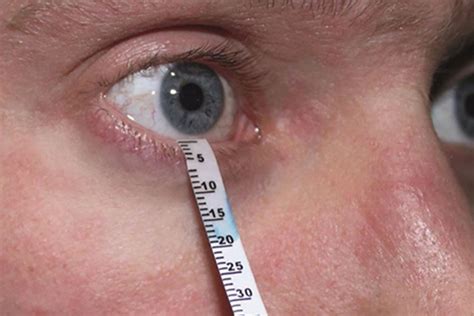
The test works by the principle of capillary action, which allows the water in tears to travel along the length of a paper test strip in an identical fashion as a horizontal capillary tube. The rate of travel along the test strip is proportional to the rate of tear production. The patient is instructed to look upward, and the patient’s eyelid is pulled down. The bent end of the test strip is placed in the e.
The Schirmer test is objectively used to measure tear secretion. The test is performed by placing a porous filter strip in the inferior fornix of each unanesthetized eye for 10 minutes. A healthy .
Schirmer's test measures total tear secretion, including reflex, and basal tears. The test is known to measure reflex tears without anesthesia and basal tears with anesthesia ( 23 – 25 ). .The Schirmer tear test performed with and without anesthesia evaluates tear adequacy and often aids in the diagnosis of dry eye syndrome. The Schirmer test performed without anesthesia .Schirmer's test is used to determine whether the eye produces enough tears to keep it moist. The test is performed by placing filter paper inside the lower lid of the eye. After 5 minutes, the .
The Basic Tear Secretion Test is used to measure basal tear volume (without reflex component). They are tools that can be used as part of a dry eye workup. Indications. Patient complaint of .
(Schirmer’s test is also known as the dry eye test, the tear — or tearing — test and the basal secretion test.) The eyes’ natural tears are produced by special cells in the conjunctiva and by the lacrimal and meibomian glands. The Schirmer tear test assesses the amount of tears in the eyes and is frequently used to diagnose dry eye syndrome. Basal and reflex tear secretion are measured together using the non-anesthetized Schirmer test or when the test is carried out without anesthesia.
There are two variations of the Schirmer test: Schirmer I measures total tear secretion (basal and reflex). Schirmer II is a measure of reflex secretion only and involves nasal stimulation following insertion of the strip. There is some debate about the reliability of testing to evaluate tear production, but we find it useful to assess the basal tear secretion. This is done by placing a strip of filter paper in the conjunctival fornix after administering topical anesthetic drops.Schirmer's test uses paper strips inserted into the eye for several minutes to measure the production of tears. Both eyes are tested at the same time. Most often, this test consists of placing a small strip of filter paper inside the lower eyelid (inferior fornix).The Schirmer test is objectively used to measure tear secretion. The test is performed by placing a porous filter strip in the inferior fornix of each unanesthetized eye for 10 minutes. A healthy eye should wet more than 15 mm of the standard filter strip in 5 minutes.
Schirmer's test measures total tear secretion, including reflex, and basal tears. The test is known to measure reflex tears without anesthesia and basal tears with anesthesia ( 23 – 25 ). However, the concept of basal tears is uncertain.Schirmer's test is used to determine whether the eye produces enough tears to keep it moist. The test is performed by placing filter paper inside the lower lid of the eye. After 5 minutes, the paper is removed and tested for its moisture content.
Schirmer's test
The Basic Tear Secretion Test is used to measure basal tear volume (without reflex component). They are tools that can be used as part of a dry eye workup. Indications. Patient complaint of dry eyes or suspected dry eyes. Contra-Indications. Allergy to topical ocular anesthetic, if used. Materials. Schirmer Tear Test strips.The Schirmer tear test performed with and without anesthesia evaluates tear adequacy and often aids in the diagnosis of dry eye syndrome. The Schirmer test performed without anesthesia measures basal tear secretion and reflex tear secretion. (Schirmer’s test is also known as the dry eye test, the tear — or tearing — test and the basal secretion test.) The eyes’ natural tears are produced by special cells in the conjunctiva and by the lacrimal and meibomian glands. The Schirmer tear test assesses the amount of tears in the eyes and is frequently used to diagnose dry eye syndrome. Basal and reflex tear secretion are measured together using the non-anesthetized Schirmer test or when the test is carried out without anesthesia.
There are two variations of the Schirmer test: Schirmer I measures total tear secretion (basal and reflex). Schirmer II is a measure of reflex secretion only and involves nasal stimulation following insertion of the strip.
There is some debate about the reliability of testing to evaluate tear production, but we find it useful to assess the basal tear secretion. This is done by placing a strip of filter paper in the conjunctival fornix after administering topical anesthetic drops.Schirmer's test uses paper strips inserted into the eye for several minutes to measure the production of tears. Both eyes are tested at the same time. Most often, this test consists of placing a small strip of filter paper inside the lower eyelid (inferior fornix).The Schirmer test is objectively used to measure tear secretion. The test is performed by placing a porous filter strip in the inferior fornix of each unanesthetized eye for 10 minutes. A healthy eye should wet more than 15 mm of the standard filter strip in 5 minutes.Schirmer's test measures total tear secretion, including reflex, and basal tears. The test is known to measure reflex tears without anesthesia and basal tears with anesthesia ( 23 – 25 ). However, the concept of basal tears is uncertain.
Schirmer's test is used to determine whether the eye produces enough tears to keep it moist. The test is performed by placing filter paper inside the lower lid of the eye. After 5 minutes, the paper is removed and tested for its moisture content.The Basic Tear Secretion Test is used to measure basal tear volume (without reflex component). They are tools that can be used as part of a dry eye workup. Indications. Patient complaint of dry eyes or suspected dry eyes. Contra-Indications. Allergy to topical ocular anesthetic, if used. Materials. Schirmer Tear Test strips.
However, running an autoclave necessitates meticulous attention to detail in order to obtain best sterilizing outcomes. In this article, we will explore the topic of how to use an autoclave effectively and safely, providing .This Instructable will cover the materials and methods necessary to sterilize things at home using a pressure cooker as an autoclave.
basal tear secretion test|The Tearing Patient: Diagnosis and Management